Biology of Reproduction, lecture on Adult Male Reproductive Systems
X. Adult Male
A. Reproductive Anatomy
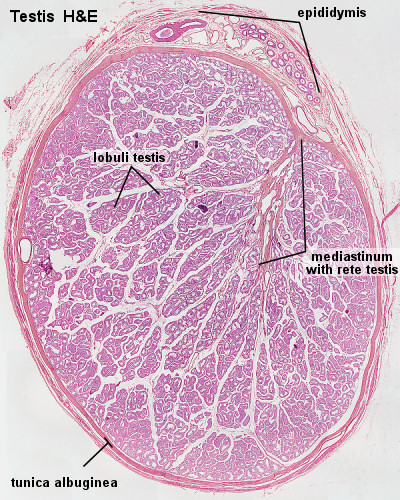
1. Testes
a. Seminiferous tubules
i. where spermatogenesis &
spermiogenesis take place
ii. coiled loops
b. Lobule
i. 250/testis;
1-3 closed coiled loops/lobule
c. Tubulus Rectus
d. Rete Testis
e.Vasa Efferentia
2. Epididymis
a. Site of Sperm Storage
b. Head
c. Body
d. Tail
i. Ductus Epididymis
3. Vas Deferens
a. transport of ejaculate
B. Seminiferous Tubule Function
1. Interstitium
a. Leydig Cells
i. synthesize steroid hormones (D5(similar))
(1) Major: Testosterone (T)
(2) Other: Androstenedione, DHEA,
5a-DHT (5a-Dihydrotestosterone)
(a) also very small amounts of estradiol
ii. homologous to theca
b. blood vessels & connective tissue
2. Seminiferous Epithelium
a. Spermatogonia produced throughout life
i. 2N, mitosis
b. 1o Spermatocytes (2N)
i. Meiosis I
c. 2o Spermatocytes (N)
i. Meiosis II
d. Spermatid (N)
e. Spermatozoa
i. Sertoli Cells
(1) provide nutrients for spermatozoa,
secrete ABP (androgen binding protein),
phagocytosis of degenerated germ cells
(2) produce testicular fluid ® into lumen
(3) homologous to granulosa cells
3. Spermatogenesis: a ® d
a. making of spermatogonia ® spermatids
4. Spermiogenesis: d ® e
a. spermatid to spermatozoa
5. Spermiation
a. sperm being released from sertoli cell into lumen
PROCESS |
STRUCTURE |
HORMONE NECESSARY |
|
Spermatogonia |
|
| mitosis |
¯ |
FSH and/or T |
|
Spermatogonia |
|
Meiosis I
Spermatogenesis |
¯ |
? |
|
1o Spermatocytes |
|
Meiosis I
Spermatogenesis |
¯ |
T |
|
2o Spermatocytes |
|
Meiosis II
Spermatogenesis |
¯ |
T |
|
Spermatid (N) |
|
| Spermiogenesis |
¯ |
FSH |
|
Spermatozoa (N) |
|
| Spermiation |
¯ |
LH (just like ovulation) |
|
released Spermatozoa (N) |
|